Hydrogen leakage monitoring
Enhancing Safety in Thermal Power Plants: The Imperative of Hydrogen Leakage Monitoring
Hydrogen plays a crucial role in the operation of thermal power plants, particularly in cooling systems for generators. While offering efficiency benefits, the use of hydrogen also introduces significant safety risks, primarily due to its highly flammable nature. In this context, hydrogen leakage monitoring is not just a safety measure but a critical component ensuring the continuous, safe operation of thermal power facilities. This blog explores the challenges and solutions associated with implementing effective hydrogen leak detection systems in the unique environment of thermal power generation.
In thermal power plants, hydrogen is often used as a cooling agent in generators due to its excellent thermal conductivity properties. However, its flammability and invisibility make hydrogen leaks a potent risk, potentially leading to fires or explosions if mixed with air in sufficient concentrations. This section underscores the importance of proactive leakage monitoring to prevent such hazardous incidents and ensure the plant’s operational safety and efficiency.
NA1 Portable hydrogen leak Detector
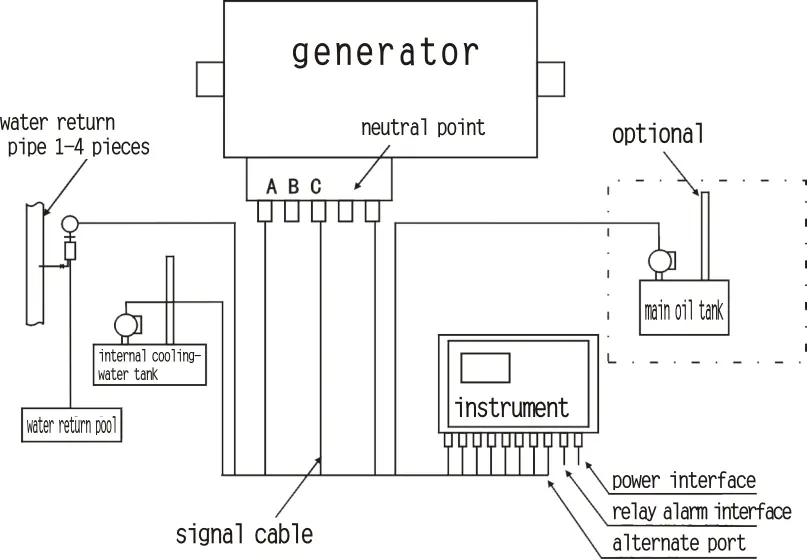
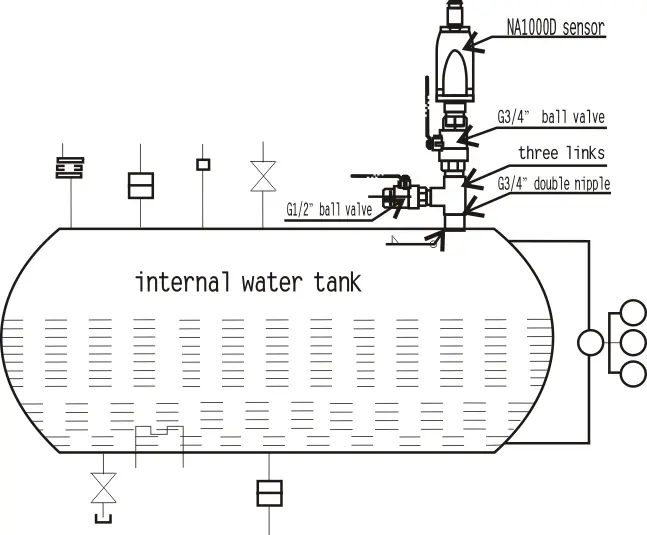
NA1000D hydrogen leakage monitoring system
Designed specifically for locations such as generator seal rings, neutral points, return oil systems for steam turbine excitation ends, internal cooling water tanks, etc., the sampling system varies according to the positions of different field measurement points.
The transmitter features a fully metallic explosion-proof housing, meeting explosion protection class ExiaⅡCT4Ga.